Проблемы с рендерингом карт Quake 3
Я работал над загрузчиком Quake 3 BSP. Однако я не могу заставить лица правильно рендериться.
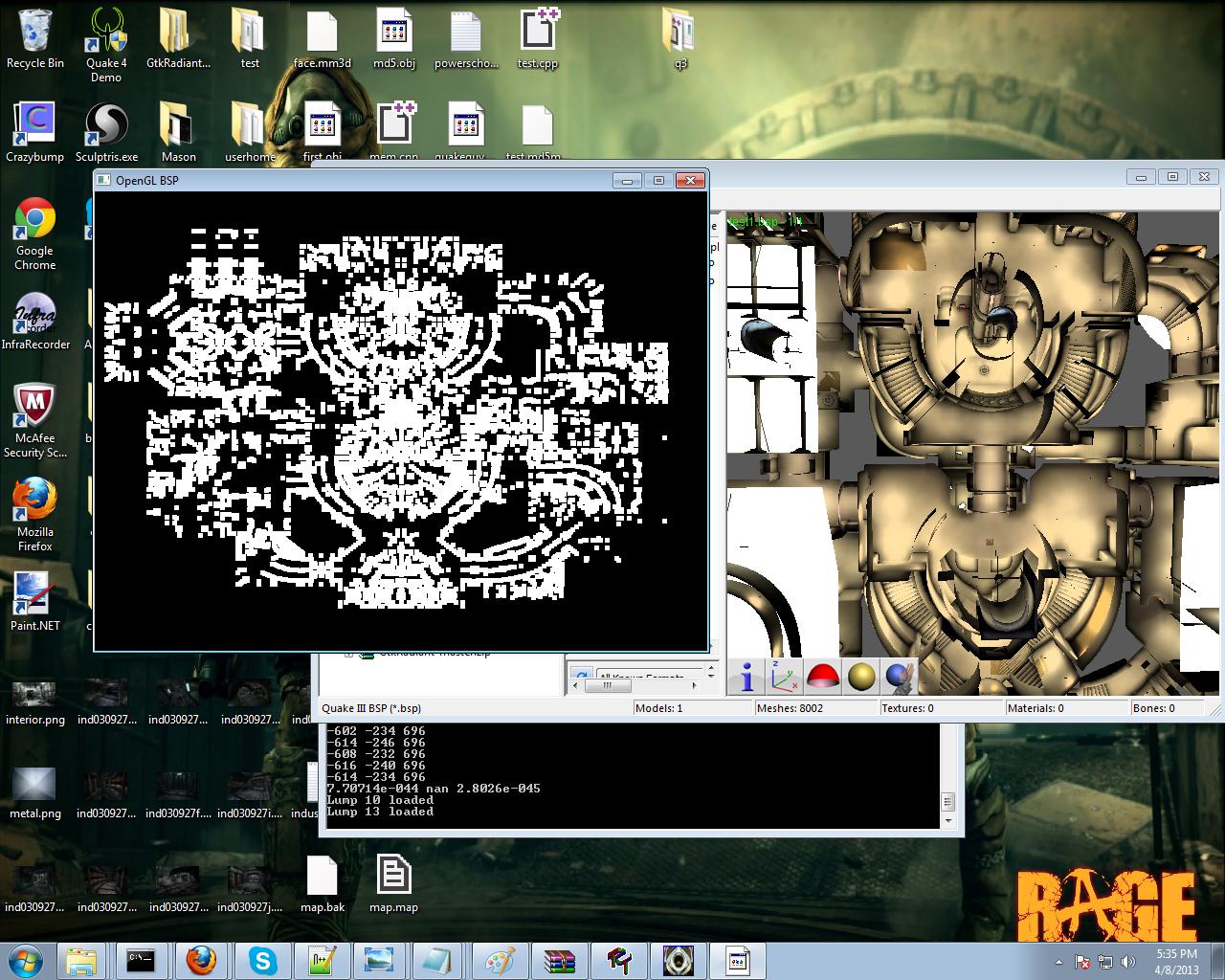
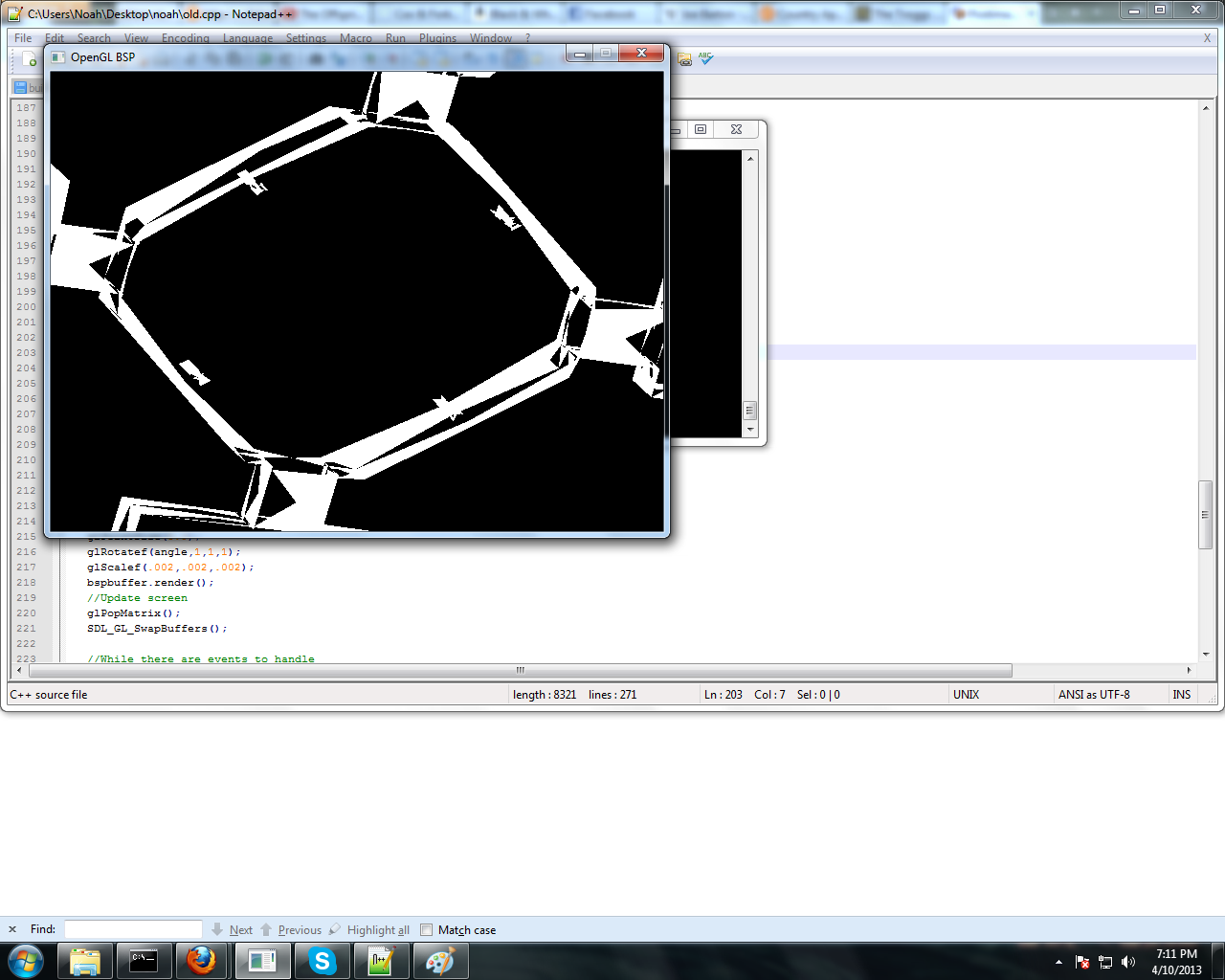
Вот вершины для карты. Вот что происходит, когда я рисую лица на карте.
Это код для рендеринга:
void bsp::render()
{
for ( int j = 0; j <= bsp::lumps[13].length/sizeof(bspface); j++)//Read until end of lump
{
if ((bsp::faces[j].type == 1)||(bsp::faces[j].type == 3)) // 1=polygon, 2=patch, 3=mesh, 4=billboard
{
glFrontFace(GL_CW);
glBegin(GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP);
for ( int k = 0; k <= bsp::faces[j].numofverts - 1; k++)//Read until end of lump
{
glVertex3f(bsp::vertices[bsp::faces[j].vertexindex+k].position.x, bsp::vertices[bsp::faces[j].vertexindex+k].position.y, bsp::vertices[bsp::faces[j].vertexindex+k].position.z);
}
glEnd();
}
}
}
Полный исходный код:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sstream>
#include <GL/GL.h>
#include <SDL/SDL.h>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;
int SCREEN_WIDTH = 640;
int SCREEN_HEIGHT = 480;
int SCREEN_BPP = 24;
bool running = true;
bool lightmaps;
SDL_Event event;
#define MAX_BRUSHES 10000
#define MAX_FACES 10000
#define MAX_VERTS 10000000
#define MAX_TEXTURES 1000
#define MAX_LEAFFACES 65536
struct pos
{
float x;
float y;
float z;
};
struct bspface
{
int textureid; // The index into the texture array
int effect; // The index for the effects (or -1 = n/a)
int type; // 1=polygon, 2=patch, 3=mesh, 4=billboard
int vertexindex; // The index into this face's first vertex
int numofverts; // The number of vertices for this face
int meshvertindex; // The index into the first meshvertex
int nummeshverts; // The number of mesh vertices
int lightmapid; // The texture index for the lightmap
int lmapcorner[2]; // The face's lightmap corner in the image
int lmapsize[2]; // The size of the lightmap section
float lmappos[3]; // The 3D origin of lightmap.
float lmapbitsets[2][3]; // The 3D space for s and t unit vectors.
float vnormal[3]; // The face normal.
int size[2]; // The bezier patch dimensions.
};
struct bspvertex
{
pos position; //x y z
float texturecoord[2]; //u, v texture coordinate
float lightmapcoord[2]; //u, v lightmap coordinate
float normal[3]; //x, y, z normalized vector
char color[4]; //RGBA color for the vertex
};
struct bsptexture
{
char name[64]; // The name of the texture w/o the extension
int flags; // The surface flags (unknown)
int contents; // The content flags (unknown)
};
struct bspbrush
{
int brushSide; // The starting brush side for the brush
int numofbrushsides; // Number of brush sides for the brush
int textureid; // The texture index for the brush
};
struct bsplump
{
int offset;
int length;
};
class bsp
{
public:
ifstream bspfile;
bsplump lumps[16];
char entities[10000];
bspvertex vertices[MAX_VERTS];
bspface faces[MAX_FACES];
bsptexture textures[MAX_TEXTURES];
bspbrush brushs[MAX_BRUSHES];
int faceindex[MAX_LEAFFACES];
void load(string);
void render();
};
void bsp::load(string name)
{
cout << "Loading BSP \"" << name << "\"" << endl;
bsp::bspfile.open (name.c_str(), istream::binary);
if(bsp::bspfile == NULL)
cout << "ERROR: No file named \""<< name <<"\" found" << endl;
else
{
char magic[64]; //Number used in Quake 3 BSP header
bsp::bspfile.read(magic, 4); //Read the magic number in the header of the BSP file it should be "IBSP"if((magic[0] != 'I')||(magic[1] != 'B')||(magic[2] != 'S')||(magic[3] != 'P'))
{
cout << "ERROR: Not a valid Quake 3 BSP file" << endl;
}
else
{
int version;
char vbuffer[4];
bsp::bspfile.read(vbuffer, 4);
for ( int k = 0; k <= 3; k++)
{
((char*)&version)[k] = vbuffer[k];
}
if(version != 46)//46 = 0x2e in hexidecimal
cout << "ERROR: Unknown version of Quake 3 BSP" << endl;
else
{
for ( int i = 0; i <= 16; i++)
{
char lumpoffset[4];
char lumplength[4];
//Read lumps offset
bsp::bspfile.read(lumpoffset, 4);
for ( int k = 0; k <= 3; k++)
{
((char*)&bsp::lumps[i].offset)[k] = lumpoffset[k];
}
//Read lumps length
bsp::bspfile.read(lumplength, 4);
for ( int k = 0; k <= 3; k++)
{
((char*)&bsp::lumps[i].length)[k] = lumplength[k];
}
cout << "Lump " << i << " offset is " << bsp::lumps[i].offset << endl
<< "Lump " << i << " length is " << bsp::lumps[i].length << endl << endl;
}
//Load entities (LUMP 0)
bsp::bspfile.seekg (bsp::lumps[0].offset, ios::beg);
bsp::bspfile.read(bsp::entities, bsp::lumps[0].length);
//Load textures (LUMP 1)
bsp::bspfile.seekg (bsp::lumps[1].offset, ios::beg);
for ( int j = 0; j <= bsp::lumps[1].length/sizeof(bsptexture); j++) //Read until end of lump
{
char buffer[72];
bsp::bspfile.read(buffer, 72);
for ( int k = 0; k <= 71; k++)//Read until end of lump
{
((char*)&bsp::textures[j])[k] = buffer[k];
}
}
//Load Leaffaces (LUMP 5)
bsp::bspfile.seekg (bsp::lumps[5].offset, ios::beg);
for ( int j = 0; j <= bsp::lumps[5].length/sizeof(bspvertex); j++) //Read until end of lump
{
char buffer[4]; //create buffer for Leaffaces
bsp::bspfile.read(buffer, 4); //Read
for ( int k = 0; k <= 3; k++) //Read until end of lump
{
((char*)&bsp::faceindex[j])[k] = buffer[k];
}
}
//Load vertices (LUMP 10)
bsp::bspfile.seekg (bsp::lumps[10].offset, ios::beg); //Load vertex data from vertex lump (10)
for ( int j = 0; j <= bsp::lumps[10].length/sizeof(bspvertex); j++)//Read until end of lump
{
char buffer[44]; //create buffer for verts
bsp::bspfile.read(buffer, 44); //Read
for ( int k = 0; k <= 43; k++)//Read until end of lump
{
((char*)&bsp::vertices[j])[k] = buffer[k];
}
}
//Load faces (LUMP 13)
bsp::bspfile.seekg (bsp::lumps[13].offset, ios::beg); //Load face data from face lump (13)
for ( int j = 0; j <= bsp::lumps[13].length/sizeof(bspface); j++)//Read until end of lump
{
char buffer[104]; //create buffer for faces
bsp::bspfile.read(buffer, 104); //Read
for ( int k = 0; k <= 103; k++) //Read until end of lump
{
((char*)&bsp::faces[j])[k] = buffer[k];
}
}
}
}
}
}
void bsp::render()
{
for ( int j = 0; j <= bsp::lumps[13].length/sizeof(bspface); j++)//Read until end of lump
{
if ((bsp::faces[j].type == 1)||(bsp::faces[j].type == 3)) // 1=polygon, 2=patch, 3=mesh, 4=billboard
{
glFrontFace(GL_CW);
glBegin(GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP);
for ( int k = 0; k <= bsp::faces[j].numofverts - 1; k++)//Read until end of lump
{
glVertex3f(bsp::vertices[bsp::faces[j].vertexindex+k].position.x, bsp::vertices[bsp::faces[j].vertexindex+k].position.y, bsp::vertices[bsp::faces[j].vertexindex+k].position.z);
}
glEnd();
}
}
}
bsp bspbuffer;
bool initGL()
{
//Initialize Projection Matrix
glMatrixMode( GL_PROJECTION );
glLoadIdentity();
//Initialize Modelview Matrix
glMatrixMode( GL_MODELVIEW );
glLoadIdentity();
//Initialize clear color
glClearColor( 0.f, 0.f, 0.f, 1.f );
//glPolygonMode( GL_FRONT_AND_BACK, GL_LINE );
return true;
}
float angle;
void render()
{
angle = angle + 1;
glPushMatrix();
//Clear color buffer
glClear( GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT );
//Render quad
glPointSize(5.0);
glRotatef(angle,1,1,1);
glScalef(.002,.002,.002);
bspbuffer.render();
//Update screen
glPopMatrix();
SDL_GL_SwapBuffers();
//While there are events to handle
while( SDL_PollEvent( &event ) )
{
if(event.type == SDL_QUIT)
{
running = false;
exit(0);
}
}
SDL_Delay( 1000 / 30 );
}
bool init()
{
//Initialize SDL
if( SDL_Init( SDL_INIT_EVERYTHING ) < 0 )
{
return false;
}
//Create Window
if( SDL_SetVideoMode( SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT, SCREEN_BPP, SDL_OPENGL ) == NULL )
{
return false;
}
//Initialize OpenGL
if( initGL() == false )
{
return false;
}
//Set caption
SDL_WM_SetCaption( "OpenGL BSP", NULL );
return true;
}
#undef main
int main()
{
init();
bspbuffer.load("test1.bsp");
do
{
render();
}while(running);
return 0;
}
Решение
Индекс, который вы используете, указывает на полигон граней из вершин. Если вы просто хотите увидеть визуализированную карту, попробуйте заменить режим GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP на GL_POLYGON.
Треугольная версия этого многоугольника хранится в единой ячейке. Таким образом, для рендеринга треугольников вам нужны индексы, хранящиеся в meshverts и смещенные от вершинного индекса грани.
Другие решения
Для рендеринга граней как типа 1, так и типа 3 я рекомендую использовать GL_TRIANGLES с сетчатыми швами в виде кусочка 11. Это необходимо для граней типа 3, но работает и для типа 1, так что вы также можете использовать один и тот же код для обеих сторон. В вашем цикле на j вы захотите что-то вроде:
bspface *face = &bsp::faces[j];
int v = face->vertexindex;
int m = face->meshvertindex;
int n = face->nummeshverts;
glBegin(GL_TRIANGLES);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
bspvertex *vertex = &bsp::vertices[v + bsp::meshverts[m + i]];
glVertex3f(vertex->position.x, vertex->position.y, vertex->position.z);
}
glEnd();
Это, конечно, предполагает, что вы добавляете мешверты в ваш класс BSP.
Мешверты описаны как часть Q3 Характеристики карты, Я уверен, что вы видели.