Ханойские башни с рекурсией и векторами
Я работаю над «Ханойскими башнями» для школы, которая в конечном итоге займет 7 дисков, и я не могу понять, как использовать операторы cout для отображения ходов, которые делают диски. Например, «Переместить диск 7 из peg1 в peg3». Любая помощь по этому вопросу будет высоко ценится. Операторы cout будут в функциях moveDisk () и Hanoi ().
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std;
struct pegType
{
vector<int> diskStack;
string pegName;
};
/***********************Function Prototypes************************/
void loadDisk(int totalDisks, vector<int>& startPeg);
void printPeg(vector<int> stack, string name);
void moveDisk(vector<int>& startPeg, vector<int>& goalPeg);
int hanoi(int totalDisks, vector<int>& startPeg, vector<int>& goalPeg, vector<int>& tempPeg);int main()
{
//Local Variables
pegType peg1, peg2, peg3;
peg1.pegName = "Peg1";
peg2.pegName = "Peg2";
peg3.pegName = "Peg3";
const int NUM_DISKS(3);
int totalMoves = 0;//Welcome Message
cout << "Welcome to the Tower of Hanoi Simulator. This simulation will run with " << NUM_DISKS << " discs." << endl << endl;
loadDisk(NUM_DISKS, peg1.diskStack);
//Check the conditions of the pegs in the beginning
cout << "The Starting Conditions of the three pegs: ";
cout << endl; printPeg(peg1.diskStack, peg1.pegName);
printPeg(peg2.diskStack, peg2.pegName);
printPeg(peg3.diskStack, peg3.pegName);
cout << endl << "Moves required to move " << NUM_DISKS << " discs from " << peg1.pegName << " to " << peg3.pegName << ": " << endl;
totalMoves = hanoi(NUM_DISKS, peg1.diskStack, peg3.diskStack, peg2.diskStack);//Ending Conditions of the pegs and disks
cout << endl << "The Ending Conditions of the three pegs: " << endl;
printPeg(peg1.diskStack, peg1.pegName);
printPeg(peg2.diskStack, peg2.pegName);
printPeg(peg3.diskStack, peg3.pegName);
cout << endl << "A stack of " << NUM_DISKS << " can be transfered in " << totalMoves << " moves.";
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
/***********************Function Definitions*****************************/
//Load the discs into the vector
void loadDisk(int totalDisks, vector<int>& startPeg)
{
for (int i = totalDisks; i > 0; i--)
{
startPeg.push_back(i);
}
}
//Print the disk Numbers backwards (3, 2, 1) to the user
void printPeg(vector<int> stack, string name)
{
if (stack.size() > 1)
{
cout << name << " has " << stack.size() << " discs: ";
assert(stack.size() > 0);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < stack.size(); i++)
{
cout << stack[i] << " ";
}
}
else
{
cout << name << " has " << stack.size() << " discs: ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//Moves the bottom disk to the goal
void moveDisk(vector<int>& startPeg, vector<int>& goalPeg)
{
if (startPeg.size() > 0)
{
int temp = startPeg.back();
startPeg.pop_back();
goalPeg.push_back(temp);
}
}
//A recursive function that handles the disk transfer
//Displays the moves made
int hanoi(int totalDisks, vector<int>& startPeg, vector<int>& goalPeg, vector<int>& tempPeg)
{
int count = 0;
if (totalDisks > 0)
{
count = hanoi(totalDisks - 1, startPeg, goalPeg, tempPeg);
moveDisk(startPeg, goalPeg);
count++;
count += hanoi(totalDisks - 1, tempPeg, goalPeg, startPeg);
}
return count;
}
Решение
использование struct Peg в качестве параметров (вместо std::vector) в функциях Hanoii() а также MoveDisk() так что функция может правильно знать имена источника и назначения для печати.
struct pegType
{
vector<int> diskStack;
string pegName;
};
/***********************Function Prototypes************************/
void loadDisk(int totalDisks, vector<int>& startPeg);
void printPeg(vector<int> stack, string name);
void moveDisk(pegType& source, pegType& dest);
int hanoi(int totalDisks, pegType& source, pegType& dest, pegType& aux);int main()
{
//Local Variables
pegType peg1, peg2, peg3;
peg1.pegName = "Peg1";
peg2.pegName = "Peg2";
peg3.pegName = "Peg3";
const int NUM_DISKS(3);
int totalMoves = 0;//Welcome Message
cout << "Welcome to the Tower of Hanoi Simulator. This simulation will run with " << NUM_DISKS << " discs." << endl << endl;
loadDisk(NUM_DISKS, peg1.diskStack);
//Check the conditions of the pegs in the beginning
cout << "The Starting Conditions of the three pegs: ";
cout << endl; printPeg(peg1.diskStack, peg1.pegName);
printPeg(peg2.diskStack, peg2.pegName);
printPeg(peg3.diskStack, peg3.pegName);
cout << endl << "Moves required to move " << NUM_DISKS << " discs from " << peg1.pegName << " to " << peg3.pegName << ": " << endl;
totalMoves = hanoi(NUM_DISKS, peg1, peg3, peg2);//Ending Conditions of the pegs and disks
cout << endl << "The Ending Conditions of the three pegs: " << endl;
printPeg(peg1.diskStack, peg1.pegName);
printPeg(peg2.diskStack, peg2.pegName);
printPeg(peg3.diskStack, peg3.pegName);
cout << endl << "A stack of " << NUM_DISKS << " can be transfered in " << totalMoves << " moves.";
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
/***********************Function Definitions*****************************/
//Load the discs into the vector
void loadDisk(int totalDisks, vector<int>& startPeg)
{
for (int i = totalDisks; i > 0; i--)
{
startPeg.push_back(i);
}
}
//Print the disk Numbers backwards (3, 2, 1) to the user
void printPeg(vector<int> stack, string name)
{
if (stack.size() > 1)
{
cout << name << " has " << stack.size() << " discs: ";
assert(stack.size() > 0);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < stack.size(); i++)
{
cout << stack[i] << " ";
}
}
else
{
cout << name << " has " << stack.size() << " discs: ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//Moves the bottom disk to the goal
void moveDisk(pegType& source, pegType& dest)
{
if (source.diskStack.size() > 0)
{
int temp = source.diskStack.back();
source.diskStack.pop_back();
dest.diskStack.push_back(temp);
std::cout << "Moving disk# " << temp << " from " << source.pegName << " to " << dest.pegName << '\n';
}
}
//A recursive function that handles the disk transfer
//Displays the moves made
int hanoi(int totalDisks, pegType& source, pegType& dest, pegType& aux)
{
int count = 0;
if (totalDisks > 0)
{
count = hanoi(totalDisks - 1, source, aux, dest);
moveDisk(source, dest);
count++;
count += hanoi(totalDisks - 1, aux, dest, source);
}
return count;
}
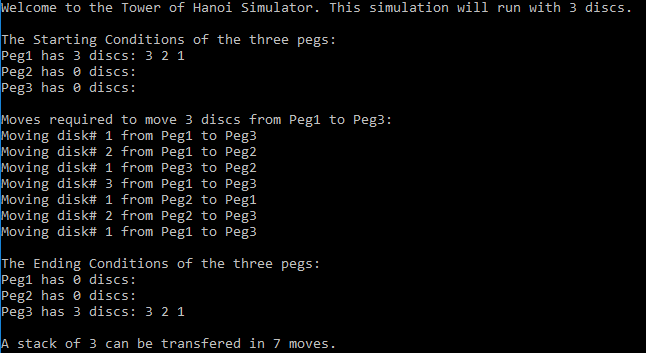
Выход:
Другие решения
Других решений пока нет …