graph — C ++ Удалить последнюю новую строку
я использую cout а также endlчтобы напечатать несколько руководств, вывод (мое намерение) будет выглядеть так:
From Spot 1
Spot 2
Spot 5
Spot 8
Spot 6
To Spot 3
Здесь, Пятно No. является случайным и генерируется из некоторых итераций. Из-за итераций я могу распечатать результат только так:
From Spot 1
Spot 2
Spot 5
Spot 8
Spot 6
Spot 3
Есть ли способ удалить мою последнюю новую строку Spot 3?
РЕДАКТИРОВАТЬ:
Я хочу найти кратчайший путь (используя алгоритм Флойда-Варшалла) между двумя вершинами. Вот мой код, и он описывает следующее:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int INF = 100000;
int n = 10, path[11][11], dist[11][11], map[11][11];
void init() {
int i, j;
for ( i = 1; i <= n; i++ )
for ( j = 1; j <= n; j++ )
map[i][j] = ( i == j ) ? 0:INF;
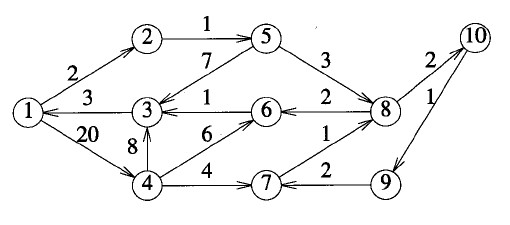
map[1][2] = 2, map[1][4] = 20, map[2][5] = 1;
map[3][2] = 3, map[4][3] = 8, map[4][6] = 6;
map[4][7] = 4, map[5][3] = 7, map[5][8] = 3;
map[6][3] = 1, map[7][8] = 1, map[8][6] = 2;
map[8][10] = 2, map[9][7] = 2, map[10][9] = 1;
}
void floyd() {
int i, j, k;
for ( i = 1; i <= n; i++ )
for ( j = 1; j <= n; j++ )
dist[i][j] = map[i][j], path[i][j] = 0;
for ( k = 1; k <= n; k++ )
for ( i = 1; i <= n; i++ )
for ( j = 1; j <= n; j++ )
if ( dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] < dist[i][j] )
dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j], path[i][j] = k;
}
void output( int i, int j ) {
if ( i == j ) return;
if ( path[i][j] == 0 ) cout << "Spot" << j << endl;
else {
output( i, path[i][j] ); // iterations
output( path[i][j], j );
}
}
int main() {
int u, v;
init();
floyd();
u = 1, v = 3;
if ( dist[u][v] == INF ) cout << "No path" << endl;
else {
cout << "From Spot" << u << endl;
output( u, v );
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Теперь проблема в том, чтобы найти условие последней итерации, чтобы я мог cout другое выражение. Но я думаю, что решить проблему проще, просто удалив последнее выражение и переписав, поэтому я не прикреплял свой код.
РЕДАКТИРОВАТЬ 2:
Я достиг своей цели с помощью Фабиана Тэмпа, хотя мне кажется немного глупым писать код выше. Здесь идет модифицированный код:
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int INF = 100000;
int n = 10, path[11][11], dist[11][11], map[11][11];
void init() {
int i, j;
for ( i = 1; i <= n; i++ )
for ( j = 1; j <= n; j++ )
map[i][j] = ( i == j ) ? 0:INF;
map[1][2] = 2, map[1][4] = 20, map[2][5] = 1;
map[3][3] = 3, map[4][3] = 8, map[4][6] = 6;
map[4][7] = 4, map[5][3] = 7, map[5][8] = 3;
map[6][3] = 1, map[7][8] = 1, map[8][6] = 2;
map[8][10] = 2, map[9][7] = 2, map[10][9] = 1;
}
void floyd() {
int i, j, k;
for ( i = 1; i <= n; i++ )
for ( j = 1; j <= n; j++ )
dist[i][j] = map[i][j], path[i][j] = 0;
for ( k = 1; k <= n; k++ )
for ( i = 1; i <= n; i++ )
for ( j = 1; j <= n; j++ )
if ( dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] < dist[i][j] )
dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j], path[i][j] = k;
}
void output( int i, int j, queue<int> &output_queue ) {
if ( i == j ) return;
if ( path[i][j] == 0 ) output_queue.push(j);
else {
output( i, path[i][j], output_queue); // iterations
output( path[i][j], j, output_queue);
}
}
void print_path(queue<int> output_queue) {
if (output_queue.empty()) return;
int item = output_queue.front();
while (!output_queue.empty()) {
item = output_queue.front();
output_queue.pop();
if (output_queue.empty()) {
cout << "To ";
}
cout << "Spot " << item << endl;
}
}
int main() {
int u, v;
init();
floyd();
u = 1, v = 3;
if ( dist[u][v] == INF ) cout << "No path" << endl;
else {
cout << "From Spot " << u << endl;
queue<int> output_queue;
output(u, v, output_queue);
print_path(output_queue);
}
return 0;
}
Результатом является руководство в самом начале. Спасибо вам всем!
Решение
Измените свою функцию вывода таким образом:
void output( int i, int j, Queue<int> &output_queue ) {
if ( i == j ) return;
if ( path[i][j] == 0 ) output_queue.push(j);
else {
output( i, path[i][j], output_queue); // iterations
output( path[i][j], j, output_queue);
}
}
Затем поменяй main():
//....
else {
Queue<int> output_queue;
output_queue.push(u);
output(u, v, output_queue);
print_path(output_queue);
}
//...
Затем добавьте print_path:
void print_path(Queue<int> output_queue) {
if (output_queue.empty()) return;
auto item = output_queue.front();
cout << "From Spot " << item << endl;
while (!output_queue.empty()) {
item = output_queue.front();
output_queue.pop();
if (output_queue.empty()) {
cout << "To ";"}
cout << "Spot " << item << endl;
}
}
Пара вещей здесь:
- Я не собирал и не проверял это. Попробуйте выяснить все ошибки самостоятельно и сообщите мне об этом в комментариях.
- Было бы очень полезно посмотреть на STL. http://www.cplusplus.com/reference отличный ресурс для этого.
- Если вы не знакомы с передача по ссылке, это стратегия, которую я использовал, чтобы убедиться, что мы добавляем информацию к тому же
output_queue, Обратите внимание, что я прошел мимо копия заprint_path()потому что это уничтожает данные в параметре. Это один из самых мощных методов в C ++.
Другие решения
если у вас есть сколько строк вы напечатали, вы можете использовать этот макрос
#define gotoxy(a,b) {COORD coord; coord.X=(b); coord.Y=(a) ; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord);}
и перейдите к этой строке и напечатайте «» для всех символов, которые вы напечатали.
Это облегчит задачу, если вы не печатаете новую строку после каждой строки. Затем вы можете вернуться и «стереть» текст в текущей строке, выдав число символов «\ b» (backspace), равное количеству символов в строке, за которым следует такое же количество пробелов (чтобы стереть был здесь). Затем вы можете вернуться к началу строки, написав «\ r», и снова написать всю строку.
